用户登录
新用户?快速注册
学圈 > 综合讨论区

笔记时间
发表于:5年前归属:综合讨论区 阅读量:14010 回复:5
Intracellular fluid (70%)
Extracellular fluid (30%)
Interstitial(22%)
Intravascular(6%)
Transcellular (2%)
Body fluid
Adult 60%
Older adult 55% eg.frail client
Infant 80%
cations
anions
Generalized edema(anasarca)
The normal osmolality of plasma is 275-295mOsm/kg(275-295mmol/kg)
Insensible loss through skin 600-800ml
lungs 400-600ml
Hypovolemia.isotonic dehydration-most common type of dehydration.
Hypotonic overhydration(=water intoxication)
Fluid Volume Deficit
Fluid Volume Excess(P82)
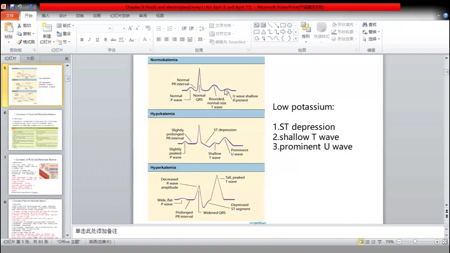
Hypokalemia
Oral potassium supplements
Liquid potassium chloride
Intravenous administered potassium
1.Never IV push,IM,H.always diluted and using an infusion device.
2.A dilution of no more than 1mEq/10ml(1mmol/10ml) of solution is recommended.
3.rotate. invert. label.
4.The maximum recommended infusion rate is 5 to 10 mEq/hour,never to exceed 20 mEq/hour.
5.More than 10 mEq/hour,cardiac monitor.
6.Phlebitis and infiltration,stopped immediately.
7.Renal function.

Hyperkalemia
1.Tall peaked T waves
2.Flat P waves
3.Widened QRS complexes
4.Prolonged PR intervals
If renal function is impaired,prepare to administer sodium polystyrene sulfonate(oral or rectal route)
Cushing’s syndrome-高钠 高压 高容 低钾 高糖
Addision’s syndrome-低钠 低压 低容 高钾 低糖
Hyponatremia
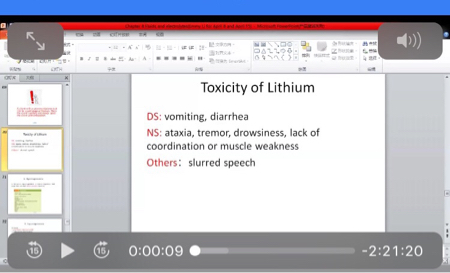
Hyponatremia precipitates lithium toxicity in a client taking lithium.

Hypernatremia(P87)
Hypocalcemia
Common Food sources
Cheese. Collard greens. Kale. Milk and soy milk. Rhubarb. Sardines. Tofu. Yogurt.
broccoli.
Chvostek’s sign
Trousseau’s sign
When administering calcium intravenously
warm the injection solution to body temperature before administration and administer slowly.
Aluminum hydroxide and Vitamin D increase calcium absorption.
Hypercalcemia(P88)
Monitor for flank or abdominal pain,and strain the urine to check for the presence of urinary stones.
A client with a calcium imbalance is at risk for a pathological fracture. More the client carefully and slowly;assist the client with ambulation.
Hypomagnesemia
Oral preparations of magnesium may cause diarrhea and increase magnesium loss.
Magnesium sulfate by the IV route(IM cause pain and tissue damage).
Calcium gluconate is the antidote for magnesium overdose.
Administer phosphorus orally along with a vitamin D supplement.
Hyperphosphatemia
Tumor lysis syndrome(TLS)
-Hyperuricemia. Hyperkalemia Hyperphosphatemia. hypocalcemia.
The normal uric acid level for a female is 2.7 to 7.3mg/dL (0.16-0.43 mmol/L) and for a male is 4.0-8.5 mg/dL(0.24-0.51 mmol/L).
Bolus(IV push)